
A direct current motor (d.c. motor) can rotate in one direction continuously. D.C. motor consists of the following parts :-
 Step 1 : At the start the coil rotates as the current flow.
Step 1 : At the start the coil rotates as the current flow.
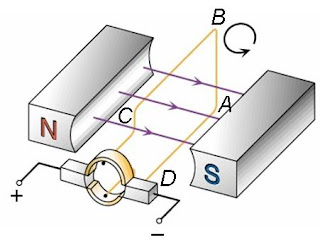 Step 2 : When the coil is at the vertical position, the coil keeps turning due to inertia.
Step 2 : When the coil is at the vertical position, the coil keeps turning due to inertia.
 Step 3 : When the coil passes the vertical position, the contacts between the half-rings & the brushes interchanges. Current in the coil is reversed. The magnetic forces acting on the coil is reversed. The coil keeps on rotating in the same direction.
Step 3 : When the coil passes the vertical position, the contacts between the half-rings & the brushes interchanges. Current in the coil is reversed. The magnetic forces acting on the coil is reversed. The coil keeps on rotating in the same direction.
Note that the commutator and the carbon brushes are arranged in such a way that the direction of the current flowing through the rectangular coil is reversed in each half of a revolution of the armature. Hence, the rectangular coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
- A permanent magnet
- A pair of carbon brushes is fixed to push against the commutator. The carbon brushes are connected to a d.c. power supply or batteries.
- An armature which is a rectangular coil bound to a soft-iron core that is placed between the poles of permanent magnet. The framework of the armature is join to an axle.
- The ends of the coil are connected to a pair of copper half-rings called a commutator (half-rings)
 Step 1 : At the start the coil rotates as the current flow.
Step 1 : At the start the coil rotates as the current flow. Step 2 : When the coil is at the vertical position, the coil keeps turning due to inertia.
Step 2 : When the coil is at the vertical position, the coil keeps turning due to inertia. Step 3 : When the coil passes the vertical position, the contacts between the half-rings & the brushes interchanges. Current in the coil is reversed. The magnetic forces acting on the coil is reversed. The coil keeps on rotating in the same direction.
Step 3 : When the coil passes the vertical position, the contacts between the half-rings & the brushes interchanges. Current in the coil is reversed. The magnetic forces acting on the coil is reversed. The coil keeps on rotating in the same direction.Note that the commutator and the carbon brushes are arranged in such a way that the direction of the current flowing through the rectangular coil is reversed in each half of a revolution of the armature. Hence, the rectangular coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
Factors that affect the speed of rotation of a d.c. motor are :-
- The strength of the permanent magnet
- The magnitude of the current
- The use of laminated soft-iron core
- The number of turns of the coil
No comments:
Post a Comment